Drug Interactions – What You Need to Know
When dealing with Drug Interactions, the way one medication can change the effect of another when taken together. Also known as drug‑drug interactions, it is a core concern for anyone on prescription or over‑the‑counter meds. Enzyme Inhibition, a process where a drug blocks the activity of metabolic enzymes often drives these changes, especially when cytochrome P450 enzymes are involved. Pharmacokinetics, the study of how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes drugs provides the framework to predict how one drug may speed up or slow down another’s clearance. Finally, Medication Side Effects, unwanted symptoms that appear after taking a drug can be magnified or hidden when interactions occur. In short, drug interactions can alter efficacy, raise toxicity risk, or render treatment useless.
Why Understanding Interactions Saves Health and Money
Most people assume that taking two pills at once is harmless, but the reality is that drug interactions often involve an enzyme‑inhibition‑induced shift in pharmacokinetics, which then changes the intensity of medication side effects. For example, combining a macrolide antibiotic like erythromycin with a statin can block CYP3A4, leading to higher statin levels and a risk of muscle damage—illustrating the triple: Drug Interactions requires knowledge of enzyme inhibition. Another common pair, an antifungal such as terbinafine and a blood‑pressure drug, shows how altered metabolism may boost blood‑level concentrations, creating a safety concern—showing that Drug Interactions encompasses changes in pharmacokinetics. Recognizing these patterns lets patients and clinicians tweak doses, switch to non‑interacting alternatives, or schedule staggered intake, which directly improves drug safety. Drug Safety, the practice of preventing adverse drug events through monitoring and education becomes the natural outcome when interactions are managed correctly.
Below you’ll find a curated set of articles that dive deep into specific drugs and how they interact with others. We cover antifungals like terbinafine, antibiotics such as erythromycin, heart medicines, hormonal pills, and even common over‑the‑counter supplements. Each post explains the mechanism, highlights real‑world examples, and offers practical steps—whether you need to adjust timing, change the dose, or pick an alternative. By reading through the collection you’ll gain a clear picture of what to watch for, how to talk to your pharmacist, and which combinations are safest for you. Armed with this knowledge, you can avoid surprises, keep your treatment effective, and stay in control of your health.

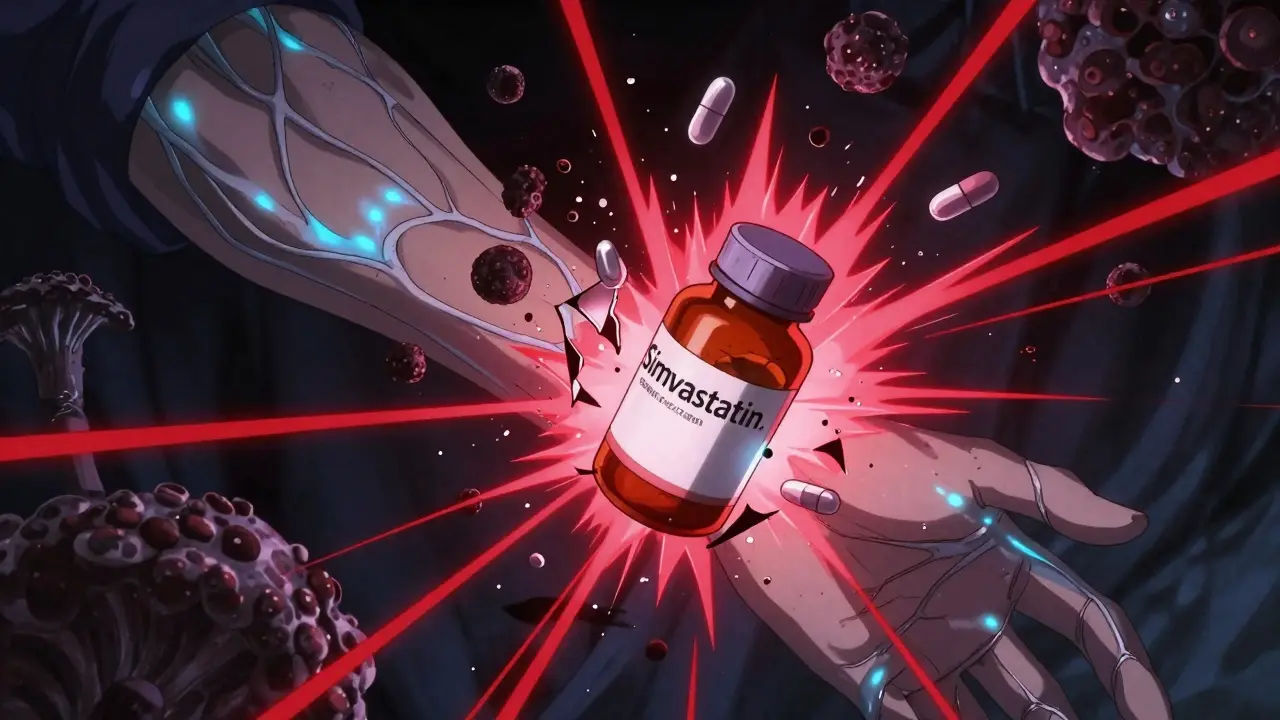
Systemic Antifungals and Statins: What You Need to Know About Dangerous Drug Interactions

Licorice Root Can Cancel Out Your Blood Pressure Medication - Here's How